Decode the transformers network
1. Introduction to Transformers
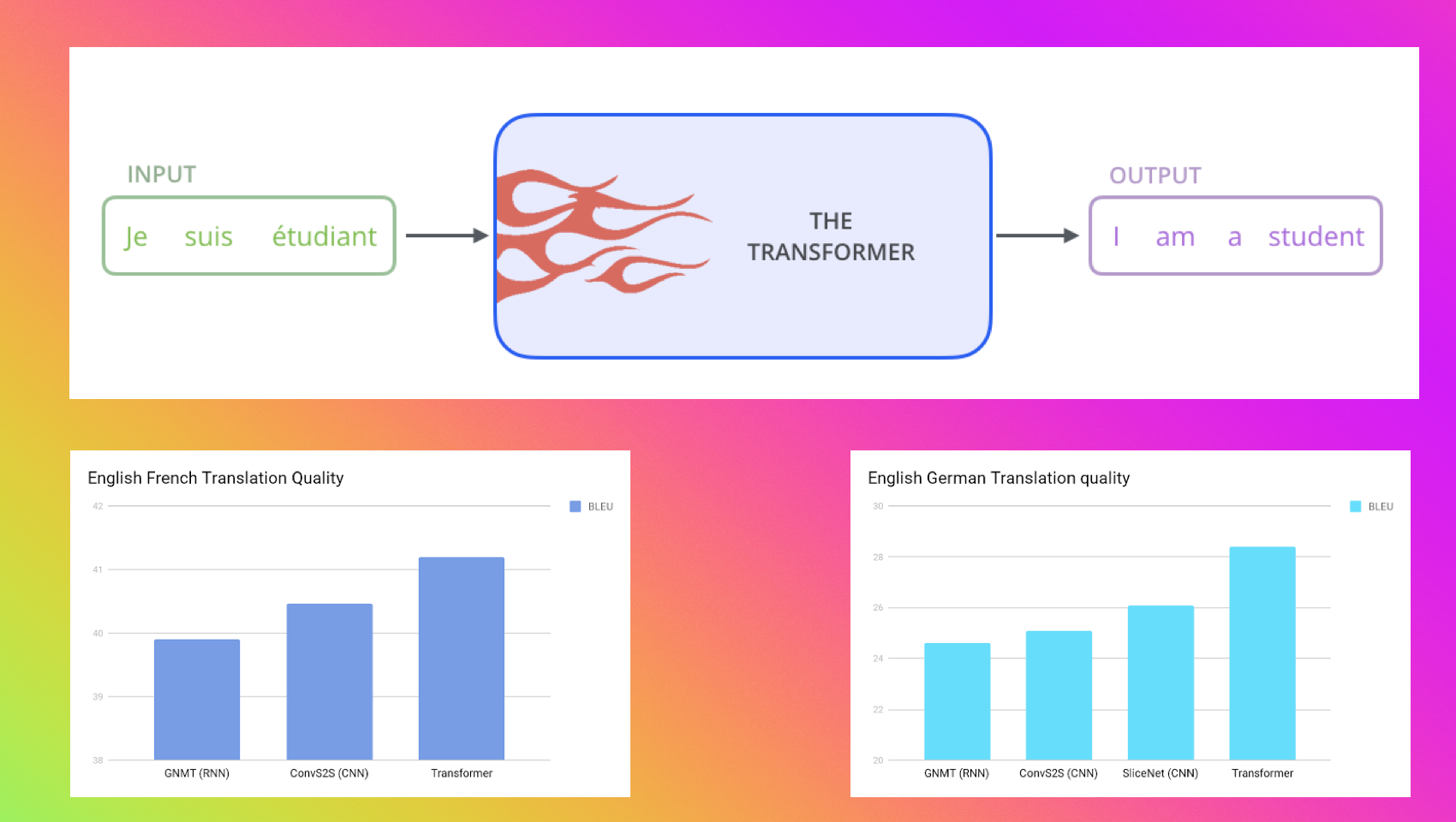
Mid 2017, the time when Attention Is All You Need paper has published by Google brains & research team. In this paper, first time transformers network, a novel neural network architecture based on a self-attention mechanism was introduced. Paper reported that transformer outperforms both recurrent and convolutional models on academic English to German and English to French translation benchmarks.
It got more highlighted in late 2018, when Google AI language team, has used transformers network and pre-trained on huge corpus of raw wikitext called BERT. This paper has reported SOTA performance on GLUE benchmark, a set of 9 diverse Natural Language Understanding (NLU) tasks and Question Answering benchmark SQuAD v1.1.
So, after this it has proven that transformers has something we should give more focus and try to use in other domains like computer vision, recommendation, time series etc. And now today we have seen that researcher is using transformers model in most of the domains.
In this blog, we will more focus of transformers basics, like self-attention, multi-head attention, tokenization, fine-tuning etc.
We will use BART a transformer based model. This model architecture is exactly same as vanilla transformers (2017), it modify ReLU to GeLUs activation functions in feed-forward layer and sine/coise based positional embeddings to learned positional embedding.(if you are not understanding this don’t worry, will able to after this blog).
from transformers.models.bart.modeling_bart import *
from transformers import BartTokenizer
from tokenizers import ByteLevelBPETokenizer
import glob
import torch
2. Tokenization
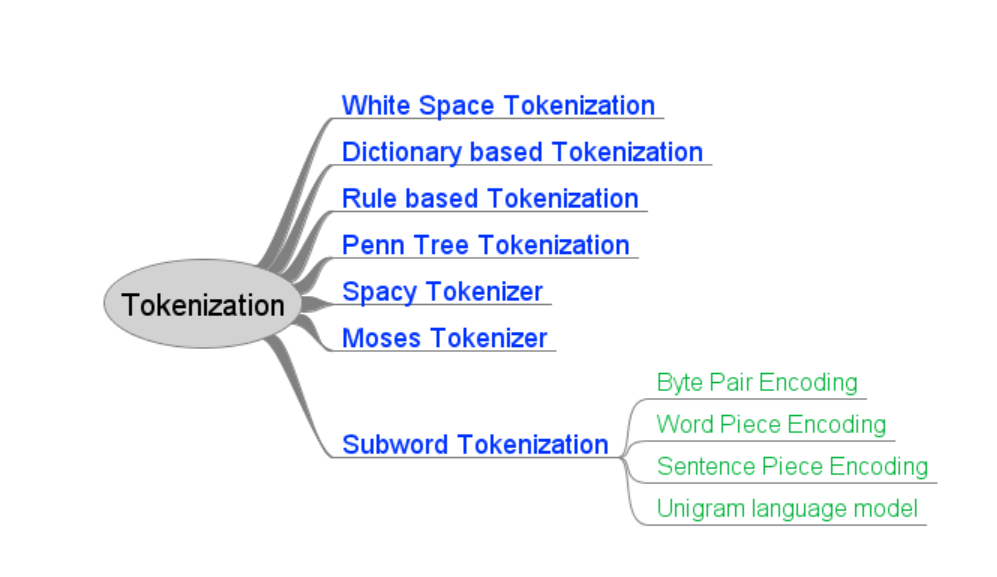
Tokenization is a process of splitting sentence into tokens. Token is single unit of information like word in sentence.
To build a tokenizer, we need to define the vocab size and few other parameters
2.1 Training
# Initialize a tokenizer
tokenizer = ByteLevelBPETokenizer()
# files
input_files = glob.glob("raw_data/*.txt")
# Customize training
tokenizer.train(files=input_files, vocab_size=1000, min_frequency=2, special_tokens=[
"<s>", #start of sentence
"<pad>", #padding token
"</s>", #end of sentence
"<unk>", #unknown words will be assigned
"<mask>", #used in self-training i.e. model pretraining
])
!mkdir sample_tokenizer
tokenizer.save_model("./sample_tokenizer")
['./sample_tokenizer/vocab.json', './sample_tokenizer/merges.txt']
2.2 Loading
# load tokenizer trained model
tokenizer = BartTokenizer.from_pretrained("sample_tokenizer/")
tokenizer
PreTrainedTokenizer(name_or_path='sample_tokenizer/', vocab_size=1000, model_max_len=1000000000000000019884624838656, is_fast=False, padding_side='right', truncation_side='right', special_tokens={'bos_token': AddedToken("<s>", rstrip=False, lstrip=False, single_word=False, normalized=True), 'eos_token': AddedToken("</s>", rstrip=False, lstrip=False, single_word=False, normalized=True), 'unk_token': AddedToken("<unk>", rstrip=False, lstrip=False, single_word=False, normalized=True), 'sep_token': AddedToken("</s>", rstrip=False, lstrip=False, single_word=False, normalized=True), 'pad_token': AddedToken("<pad>", rstrip=False, lstrip=False, single_word=False, normalized=True), 'cls_token': AddedToken("<s>", rstrip=False, lstrip=False, single_word=False, normalized=True), 'mask_token': AddedToken("<mask>", rstrip=False, lstrip=True, single_word=False, normalized=True)})
2.3 Tokenize
text = "Hi, I love NLP models."
tokenizer.tokenize(text)
['H', 'i', ',', 'ĠI', 'Ġl', 'o', 've', 'ĠNLP', 'Ġmodels', '.']
Ġ refers to a space, so that we can regenerate input text.
2.4 Encode Tokens into ids
encoded_ids = tokenizer.encode(text) # add_special_tokens=False
encoded_ids
[0, 44, 77, 16, 319, 330, 83, 374, 947, 854, 18, 2]
tokenizer.decode(encoded_ids)
'<s>Hi, I love NLP models.</s>'
<s> is the start of sentence and <s> end of the sentence.
3. Modeling
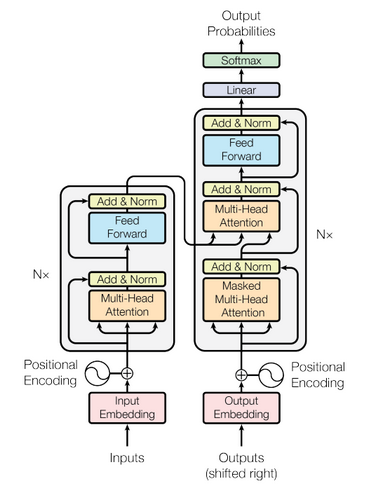
This is the vanilla transformer Architecture.
3.1 Model Configuration
In transformers, there are multiple blocks and sub blocks i.e. encoder, decoder, multi-head attention etc.
In config, we define value for the paramters of blocks/sub-blocks.
# see default settings
#BartConfig()
config = BartConfig(encoder_layers=1, decoder_layers=1, vocab_size=1000)
config
BartConfig {
"activation_dropout": 0.0,
"activation_function": "gelu",
"attention_dropout": 0.0,
"bos_token_id": 0,
"classifier_dropout": 0.0,
"d_model": 1024,
"decoder_attention_heads": 16,
"decoder_ffn_dim": 4096,
"decoder_layerdrop": 0.0,
"decoder_layers": 1,
"decoder_start_token_id": 2,
"dropout": 0.1,
"encoder_attention_heads": 16,
"encoder_ffn_dim": 4096,
"encoder_layerdrop": 0.0,
"encoder_layers": 1,
"eos_token_id": 2,
"forced_eos_token_id": 2,
"id2label": {
"0": "LABEL_0",
"1": "LABEL_1",
"2": "LABEL_2"
},
"init_std": 0.02,
"is_encoder_decoder": true,
"label2id": {
"LABEL_0": 0,
"LABEL_1": 1,
"LABEL_2": 2
},
"max_position_embeddings": 1024,
"model_type": "bart",
"num_hidden_layers": 1,
"pad_token_id": 1,
"scale_embedding": false,
"transformers_version": "4.23.1",
"use_cache": true,
"vocab_size": 1000
}
3.2 Build model from config
Lets build our first transformers model based on the above configuration.
model = BartModel(config=config)
model
BartModel(
(shared): Embedding(1000, 1024, padding_idx=1)
(encoder): BartEncoder(
(embed_tokens): Embedding(1000, 1024, padding_idx=1)
(embed_positions): BartLearnedPositionalEmbedding(1026, 1024)
(layers): ModuleList(
(0): BartEncoderLayer(
(self_attn): BartAttention(
(k_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(v_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(q_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(out_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
)
(self_attn_layer_norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(activation_fn): GELUActivation()
(fc1): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(final_layer_norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
)
)
(layernorm_embedding): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
)
(decoder): BartDecoder(
(embed_tokens): Embedding(1000, 1024, padding_idx=1)
(embed_positions): BartLearnedPositionalEmbedding(1026, 1024)
(layers): ModuleList(
(0): BartDecoderLayer(
(self_attn): BartAttention(
(k_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(v_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(q_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(out_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
)
(activation_fn): GELUActivation()
(self_attn_layer_norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(encoder_attn): BartAttention(
(k_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(v_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(q_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(out_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
)
(encoder_attn_layer_norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(fc1): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(final_layer_norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
)
)
(layernorm_embedding): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
)
)
# encoded_ids is the tokenize and encoded id of text.(see above)
# input of batch_size=1
encoded_ids = torch.tensor([encoded_ids])
encoded_ids.shape
torch.Size([1, 12])
text_feature_embeddings = model(encoded_ids).last_hidden_state
text_feature_embeddings.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
text_feature_embeddings is the feature representation of a given text input. We can use this embedding representation for our downstream tasks i.e. classification, generation, clustering etc.
4. Understand Model Layer one by one

Lets try to decode, what is happening inside the transformers network one by one block
4.1 Input Pre-processing > Word Embeddings
First step is to build word embeddings module for representing tokens in embeddings. We have defined vocab_size=1000 in tokenization module as well as in config.
Word embedding block takes input encoded id and give word representative embedding for each ids of size 1024 vector(default, we can change via config)
# model.shared
model.encoder.embed_tokens
Embedding(1000, 1024, padding_idx=1)
word_embeddings = model.encoder.embed_tokens(encoded_ids)
word_embeddings.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
4.2 Input Pre-processing > Position embeddings
As transformers take all input tokens simultaneously, not like RNN/LSTM/GRU. To capture the position of tokens, there is a position embedding block which give position embedding vector of each tokens.
There are multiple technique for position embedding i.e. sine+coise based, learned positional embedding etc.
Vanilla transformers uses sine+coise based positional embeddings but BART uses learned positional embedding.
model.encoder.embed_positions
BartLearnedPositionalEmbedding(1026, 1024)
pos_embeddings = model.encoder.embed_positions(encoded_ids)
pos_embeddings.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
4.3 Input Pre-processing > Final Inputs
input_ids = word_embeddings + pos_embeddings
input_ids.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
4.4 Encoder
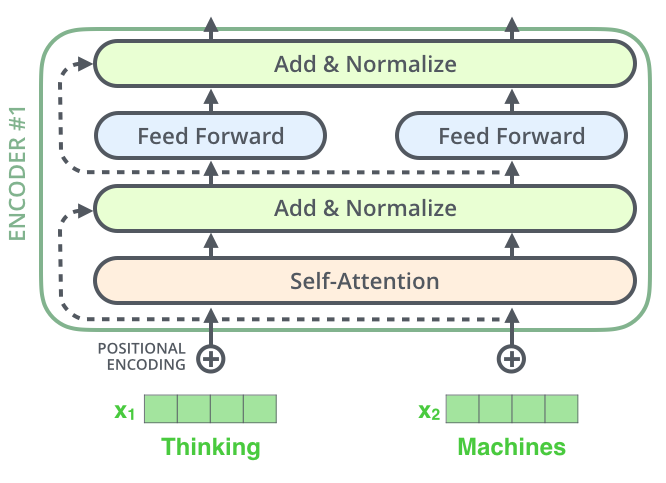

#query porjection from input_ids
model.encoder.layers[0].self_attn.q_proj(input_ids).shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
#key porjection from input_ids
model.encoder.layers[0].self_attn.k_proj(input_ids).shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
#value porjection from input_ids
model.encoder.layers[0].self_attn.v_proj(input_ids).shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
# self-attention
print(model.encoder.layers[0].self_attn(input_ids)[0].shape)
encoder_self_attn = model.encoder.layers[0].self_attn(input_ids)[0]
encoder_self_attn
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
tensor([[[-0.0034, 0.0026, 0.0081, ..., 0.0003, 0.0034, -0.0023],
[-0.0034, 0.0026, 0.0081, ..., 0.0003, 0.0034, -0.0023],
[-0.0034, 0.0026, 0.0081, ..., 0.0003, 0.0034, -0.0023],
...,
[-0.0034, 0.0026, 0.0081, ..., 0.0003, 0.0034, -0.0023],
[-0.0034, 0.0026, 0.0081, ..., 0.0003, 0.0034, -0.0023],
[-0.0034, 0.0026, 0.0081, ..., 0.0003, 0.0034, -0.0023]]],
grad_fn=<ViewBackward0>)
# Add+Norms+feedforward
encoder_self_attn_norm = model.encoder.layers[0].self_attn_layer_norm(encoder_self_attn)
encoder_self_attn_norm = model.encoder.layers[0].activation_fn(encoder_self_attn_norm)
encoder_self_attn_norm = model.encoder.layers[0].fc1(encoder_self_attn_norm)
encoder_self_attn_norm = model.encoder.layers[0].fc2(encoder_self_attn_norm)
encoder_hidden_states = model.encoder.layers[0].final_layer_norm(encoder_self_attn_norm)
encoder_hidden_states.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
model.encoder.layers[0]
BartEncoderLayer(
(self_attn): BartAttention(
(k_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(v_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(q_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(out_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
)
(self_attn_layer_norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(activation_fn): GELUActivation()
(fc1): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(final_layer_norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
)
4.5 Output Pre-processing
For decoder input, we right shift input tokens and pass through word embeddings as well as positional embeddings
encoded_ids
tensor([[ 0, 44, 77, 16, 319, 330, 83, 374, 947, 854, 18, 2]])
decoder_inputs = shift_tokens_right(encoded_ids, pad_token_id=1, decoder_start_token_id=2)
decoder_inputs
tensor([[ 2, 0, 44, 77, 16, 319, 330, 83, 374, 947, 854, 18]])
# model.shared
decoder_word_embeddings = model.decoder.embed_tokens(decoder_inputs)
decoder_word_embeddings.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
decoder_pos_embeddings = model.decoder.embed_positions(decoder_inputs)
decoder_pos_embeddings.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
decoder_input_ids = decoder_word_embeddings + decoder_pos_embeddings
decoder_input_ids.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
4.6 Decoder
model.decoder.layers[0]
BartDecoderLayer(
(self_attn): BartAttention(
(k_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(v_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(q_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(out_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
)
(activation_fn): GELUActivation()
(self_attn_layer_norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(encoder_attn): BartAttention(
(k_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(v_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(q_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(out_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=True)
)
(encoder_attn_layer_norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(fc1): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1024, bias=True)
(final_layer_norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
)
# decoder_input-decoder_input self attention
decoder_self_attn = model.decoder.layers[0].self_attn(decoder_input_ids)[0]
decoder_self_attn.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
# encoder-decoder attention i.e. cross attention
decoder_encoder_attn = model.decoder.layers[0].encoder_attn(hidden_states=decoder_self_attn,
key_value_states=encoder_hidden_states)[0]
decoder_encoder_attn.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
4.7 Output Post-Processing
# feature representation of a given input sentence
model_output_features = model(encoded_ids)
model_output_features.keys()
odict_keys(['last_hidden_state', 'past_key_values', 'encoder_last_hidden_state'])
# final feature representation
model_output_features.last_hidden_state
tensor([[[ 1.3585, 0.3638, 0.3431, ..., 1.1773, -1.6471, 0.6394],
[-0.5528, 1.0345, 0.1257, ..., -0.3872, -1.4160, 0.4665],
[-0.6704, 0.1079, 0.5481, ..., -0.1823, -0.0264, -1.1273],
...,
[ 1.3628, 1.1421, 0.8492, ..., -0.4157, 1.0859, -1.2649],
[-0.0734, 0.8632, -0.9869, ..., -0.0866, -1.4402, -0.8505],
[ 0.0052, 0.4603, 0.6000, ..., -0.5838, -0.2336, -0.3519]]],
grad_fn=<NativeLayerNormBackward0>)
# encoder last layer feature representation
model_output_features.encoder_last_hidden_state
tensor([[[ 1.0709, -1.0376, -1.3312, ..., 0.7923, -0.5834, -0.0582],
[-1.5943, -0.5630, 0.1977, ..., 0.5616, -0.6423, 1.4250],
[ 1.1451, -0.1073, 0.0637, ..., -0.7085, -0.3052, 0.7960],
...,
[-1.3538, -0.9423, -0.1416, ..., 0.9372, -0.6864, -0.1389],
[ 0.9959, -0.4869, 0.2692, ..., 0.4765, 0.1438, 1.7434],
[ 0.7082, -0.0759, -0.5594, ..., 0.4646, 0.1940, 1.9280]]],
grad_fn=<NativeLayerNormBackward0>)
4.7.1 Generative Language Model Task
Now, if you want to build a generative language model using transformers. You can take feature representation embedding from last layer of decoder and pass to the linear layer over vocab_size.
config.d_model, model.shared.num_embeddings
(1024, 1000)
# Language Model head
lm_head = torch.nn.Linear(config.d_model, model.shared.num_embeddings, bias=False)
lm_head
Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1000, bias=False)
# [batch_size, max_token_len, d_model]
lm_logits = lm_head(model_output_features[0])
lm_logits.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1000])
# loss function
loss_fct = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
loss_fct
CrossEntropyLoss()
# next words prediction i.e. target label
labels = encoded_ids
labels.shape
torch.Size([1, 12])
generative_lm_loss = loss_fct(lm_logits.view(-1, config.vocab_size), labels.view(-1))
generative_lm_loss
tensor(7.0211, grad_fn=<NllLossBackward0>)
4.7.2 Sequence Classification Task
- Single Label Classification i.e. multi class classification
- Multi Label Classification
- Regression
model_output_features.encoder_last_hidden_state.shape
torch.Size([1, 12, 1024])
# multi class classification
input_dim = 1024
inner_dim = 512
pooler_dropout=0.2
num_classes = 3
# target label
labels = torch.tensor([2])
# sentence representation from decoder last layer output
sentence_representation = model_output_features.encoder_last_hidden_state[:, -1, :]
# pooling layer
dense = torch.nn.Linear(input_dim, inner_dim)
dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(p=pooler_dropout)
#classification head
out_proj = torch.nn.Linear(inner_dim, num_classes)
sentence_representation = dense(sentence_representation)
sentence_representation = dropout(sentence_representation)
logits = out_proj(sentence_representation)
# loss function
loss_fct = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
loss = loss_fct(logits.view(-1, num_classes), labels.view(-1))
loss
tensor(1.6008, grad_fn=<NllLossBackward0>)
# multi label
input_dim = 1024
inner_dim = 512
pooler_dropout=0.2
num_classes = 3
# target label
labels = torch.tensor([[0,1,0]], dtype=torch.float32)
# sentence representation from decoder last layer output
sentence_representation = model_output_features.encoder_last_hidden_state[:, -1, :]
# pooling layer
dense = torch.nn.Linear(input_dim, inner_dim)
dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(p=pooler_dropout)
# classification head
out_proj = torch.nn.Linear(inner_dim, num_classes)
sentence_representation = dense(sentence_representation)
sentence_representation = dropout(sentence_representation)
logits = out_proj(sentence_representation)
#loss function
loss_fct = torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
loss = loss_fct(logits, labels)
loss
tensor(0.8175, grad_fn=<BinaryCrossEntropyWithLogitsBackward0>)
# regression
input_dim = 1024
inner_dim = 512
pooler_dropout=0.2
# target label
labels = torch.tensor([0.2], dtype=torch.float32)
# sentence representation from decoder last layer output
sentence_representation = model_output_features.encoder_last_hidden_state[:, -1, :]
# pooling layer
dense = torch.nn.Linear(input_dim, inner_dim)
dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(p=pooler_dropout)
# regression head
out_proj = torch.nn.Linear(inner_dim, 1)
sentence_representation = dense(sentence_representation)
sentence_representation = dropout(sentence_representation)
logits = out_proj(sentence_representation)
# loss function
loss_fct = torch.nn.MSELoss()
loss = loss_fct(logits.squeeze(), labels.squeeze())
loss
tensor(0.0389, grad_fn=<MseLossBackward0>)
5. References
- https://ai.googleblog.com/2017/08/transformer-novel-neural-network.html
- https://jalammar.github.io/illustrated-transformer/
- https://ai.googleblog.com/2018/11/open-sourcing-bert-state-of-art-pre.html
- https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
6. Cited as
@article{kumar2022decodetransformers,
title = "Decode the transformers network",
author = "Kumar, Ankur",
journal = "ankur3107.github.io",
year = "2022",
url = "https://ankur3107.github.io/blogs/decode-the-transformers-network/"
}

Comments