Mastering Language Models: Dive into the World of LLM Prompts
Dive into the World of LLM Prompts
Unleashing the power of Language Models (LLMs) involves a simple yet remarkable process: feed it a prompt and let it work its magic by generating text based on its trained patterns.
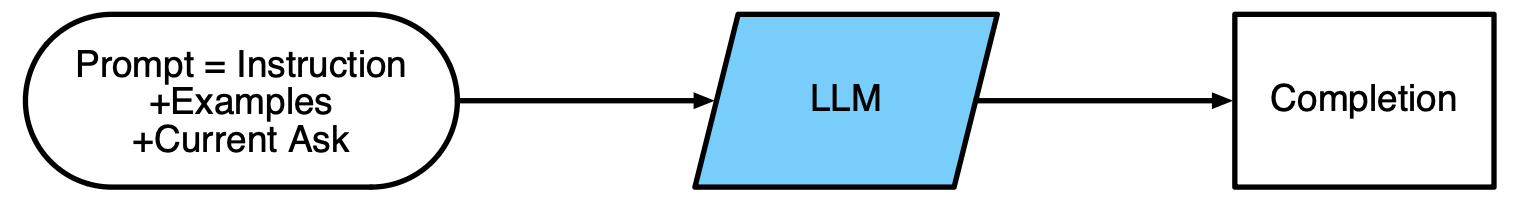
To generate text using an LLM, a prompt is typically provided to the model, which is made up of three key components: Instruction, Examples, and Current Ask.
-
Instructionis the first component of an LLM Prompt, and it refers to the specific task or goal that the model is expected to complete. This instruction should be clear and concise, so that the model understands exactly what is expected of it. -
The second component of an LLM Prompt is
Examples, which are used to provide guidance and demonstrate what is expected. Examples can take many forms, such as sample text, articles or stories. The goal of providing examples is to show the model what it should be aiming for and to give it a roadmap for how to achieve it. -
Finally, the
Current Askprompts the model to engage with the text & demonstrate understanding and complete with generation.
By blending these components together, LLM prompts provide a robust and reliable framework for generating accurate and effective text. Whether you’re writing articles, creating chatbots, or crafting conversational agents, LLM prompts are the go-to tool for delivering high-quality results.
Let’s Make A Simple Prompt Class
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import Optional
class Prompt(BaseModel):
# Define the class attributes with optional instruction and examples strings,
# and a required current_ask string. Set the separator string to "\n".
instruction: Optional[str] = None
examples: Optional[str] = None
current_ask: str
sep = "\n"
def get(self, **kwargs):
# Define the get method to generate a prompt string from the attributes,
# using string formatting with keyword arguments.
# Start with an empty prompt string.
prompt = ""
# If the instruction attribute is not None or an empty string, add it to the prompt.
if self.instruction and self.instruction != "":
prompt += self.instruction
# If the examples attribute is not None or an empty string, add it to the prompt,
# separated from the instruction by the separator string.
if self.examples and self.examples != "":
prompt += self.sep + self.examples
# Add the current_ask attribute to the prompt, separated from the examples by the separator.
prompt += self.sep + self.current_ask
# Remove any leading or trailing whitespace.
prompt = prompt.strip()
# Return the formatted prompt string.
return prompt.format(**kwargs)
def set_examples(self, example_dicts, example_template):
# Define the set_examples method to set the examples attribute from a list of dictionaries
# and an example template string.
# Loop over the list of dictionaries, apply the template string to each one, and join
# the resulting strings using the separator defined in the class.
self.examples = "\n".join([example_template.format(**ed) for ed in example_dicts])
instruction = "Please give me the sentiment of below tweet."
current_ask = "tweet:{tweet}\nsentiment: "
prompt = Prompt(instruction=instruction, current_ask=current_ask)
print(prompt.get(tweet="Just had the most amazing dinner at this new restaurant! The food was incredible and the service was top notch. Can't wait to go back!"))
Please give me the sentiment of below tweet.
tweet:Just had the most amazing dinner at this new restaurant! The food was incredible and the service was top notch. Can't wait to go back!
sentiment:
LLM Invocation: Simplifying Text Generation!
import openai
openai.api_type = "azure"
openai.api_key = "..."
openai.api_base = "https://example-endpoint.openai.azure.com"
openai.api_version = "2023-03-15-preview"
def llm(prompt):
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-divanci-003", prompt=prompt, temperature=0.0)
return completion
Let’s run the above prompt
llm(prompt.get(tweet="Just had the most amazing dinner at this new restaurant! The food was incredible and the service was top notch. Can't wait to go back!"))
Positive
Now what if you have some examples for the sentiment data. Let’s use
instruction = "Please give me the sentiment of below tweet."
current_ask = "tweet:{tweet}\nsentiment: "
example_dicts = [{"sentiment": "positive", "tweet": "I just got a new job offer and it's my dream job! I can't wait to start and see where this opportunity takes me."}, {"sentiment": "negative", "tweet": "Just got rejected from my top-choice college. I worked so hard and it's devastating to hear this news."}]
prompt = Prompt(instruction=instruction, current_ask=current_ask)
prompt.set_examples(example_dicts, example_template="tweet: {tweet}\nsentiment: {sentiment}")
print(prompt.get(tweet="Just had the most amazing dinner at this new restaurant! The food was incredible and the service was top notch. Can't wait to go back!"))
Please give me the sentiment of below tweet.
tweet: I just got a new job offer and it's my dream job! I can't wait to start and see where this opportunity takes me.
sentiment: positive
tweet: Just got rejected from my top-choice college. I worked so hard and it's devastating to hear this news.
sentiment: negative
tweet:Just had the most amazing dinner at this new restaurant! The food was incredible and the service was top notch. Can't wait to go back!
sentiment:
llm(prompt.get(tweet="Just had the most amazing dinner at this new restaurant! The food was incredible and the service was top notch. Can't wait to go back!"))
Positive
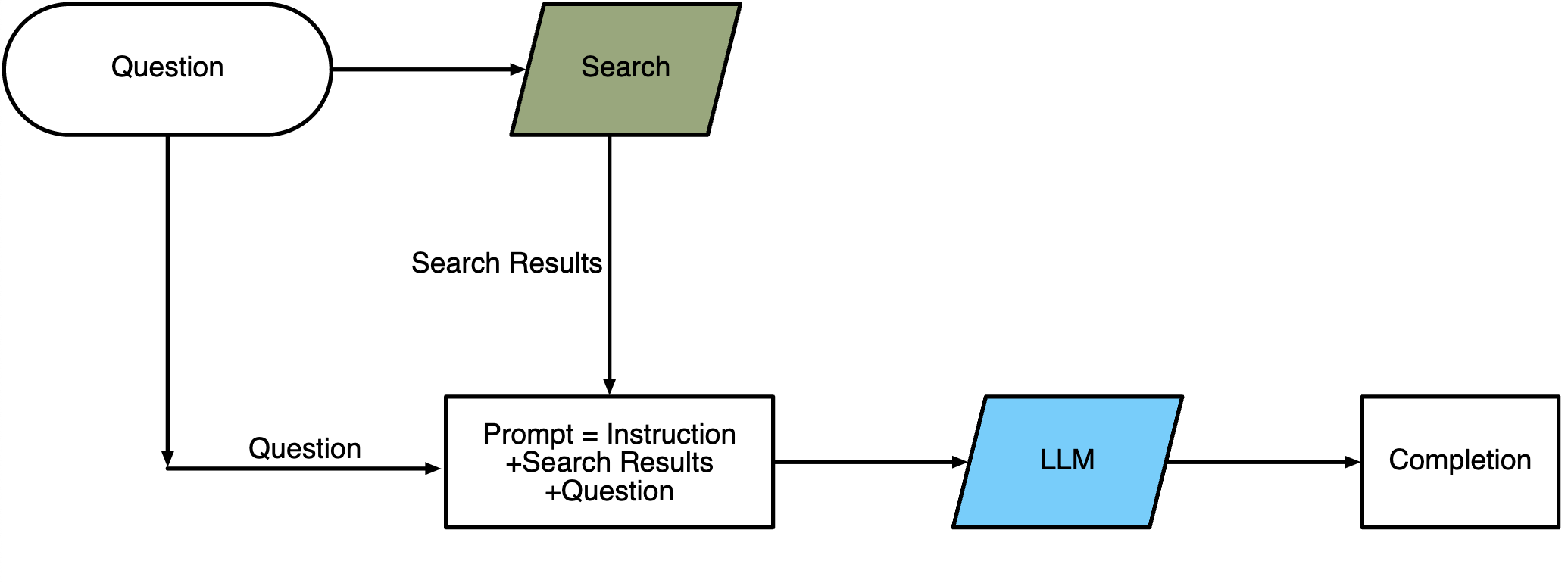
App: WebGPT
WebGPT is a technology that leverages the power of large language models (LLMs) to provide quick and accurate answers to users’ questions on the Internet. It does this by taking a user’s question and searching the Internet for relevant search results. These search results are then used as part of a prompt that is fed into an LLM, which generates an answer to the user’s question. The generated answer is then returned to the user. By combining the vast amount of information available on the Internet with the power of LLMs, WebGPT is able to provide fast and accurate answers to users’ questions.
Search using dockduckgo python wrapper
from duckduckgo_search import ddg
def search_internet(query):
results = ddg(query, safesearch='Off', max_results=3)
return "\n\n".join(["Title: "+r['title']+"\n"+"Body: "+r['body'] for r in results])
print(search_internet("Who won fifa 2022?"))
Title: Who won the 2022 FIFA World Cup? Final score, result and highlights ...
Body: Argentina are the world champions. From the moment Lionel Messi put the Copa America holders ahead in the 23rd minute of the 2022 FIFA World Cup final against France, Lionel Scaloni's side looked ...
Title: FIFA World Cup 2022: All results, scores and points table
Body: The FIFA World Cup 2022 in Qatar saw a total of 32 top national teams from five different confederations vie for the title of football world champions from November 20 to December 18.. The 2022 FIFA World Cup followed a familiar format with the 32 teams divided into eight groups - Group A to H - of four teams each. The teams in each group competed in a single-headed round-robin format in the ...
Title: Argentina Defeats France to Win 2022 World Cup Behind Lionel Messi
Body: Ryan Parker. Published on December 18, 2022 12:57 PM. Argentina has won the 2022 FIFA World Cup ! In a thrilling match that went to extra time and then a shootout between Argentina and the former ...
instruction="Use the following pieces of context to answer the question at the end. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer."
current_ask = "context:{context}\n\nquestion:{question}\nAnswer:"
prompt = Prompt(instruction=instruction, current_ask=current_ask)
question = "Who won fifa 2022?"
context = search_internet(question)
print(prompt.get(context=context, question=question))
Use the following pieces of context to answer the question at the end. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.
context:Title: Who won the 2022 FIFA World Cup? Final score, result and highlights ...
Body: Argentina are the world champions. From the moment Lionel Messi put the Copa America holders ahead in the 23rd minute of the 2022 FIFA World Cup final against France, Lionel Scaloni's side looked ...
Title: FIFA World Cup 2022: All results, scores and points table
Body: The FIFA World Cup 2022 in Qatar saw a total of 32 top national teams from five different confederations vie for the title of football world champions from November 20 to December 18.. The 2022 FIFA World Cup followed a familiar format with the 32 teams divided into eight groups - Group A to H - of four teams each. The teams in each group competed in a single-headed round-robin format in the ...
Title: Argentina Defeats France to Win 2022 World Cup Behind Lionel Messi
Body: Ryan Parker. Published on December 18, 2022 12:57 PM. Argentina has won the 2022 FIFA World Cup ! In a thrilling match that went to extra time and then a shootout between Argentina and the former ...
question:Who won fifa 2022?
Answer:
llm(prompt.get(context=context, question=question))
'Argentina won the FIFA World Cup 2022.'
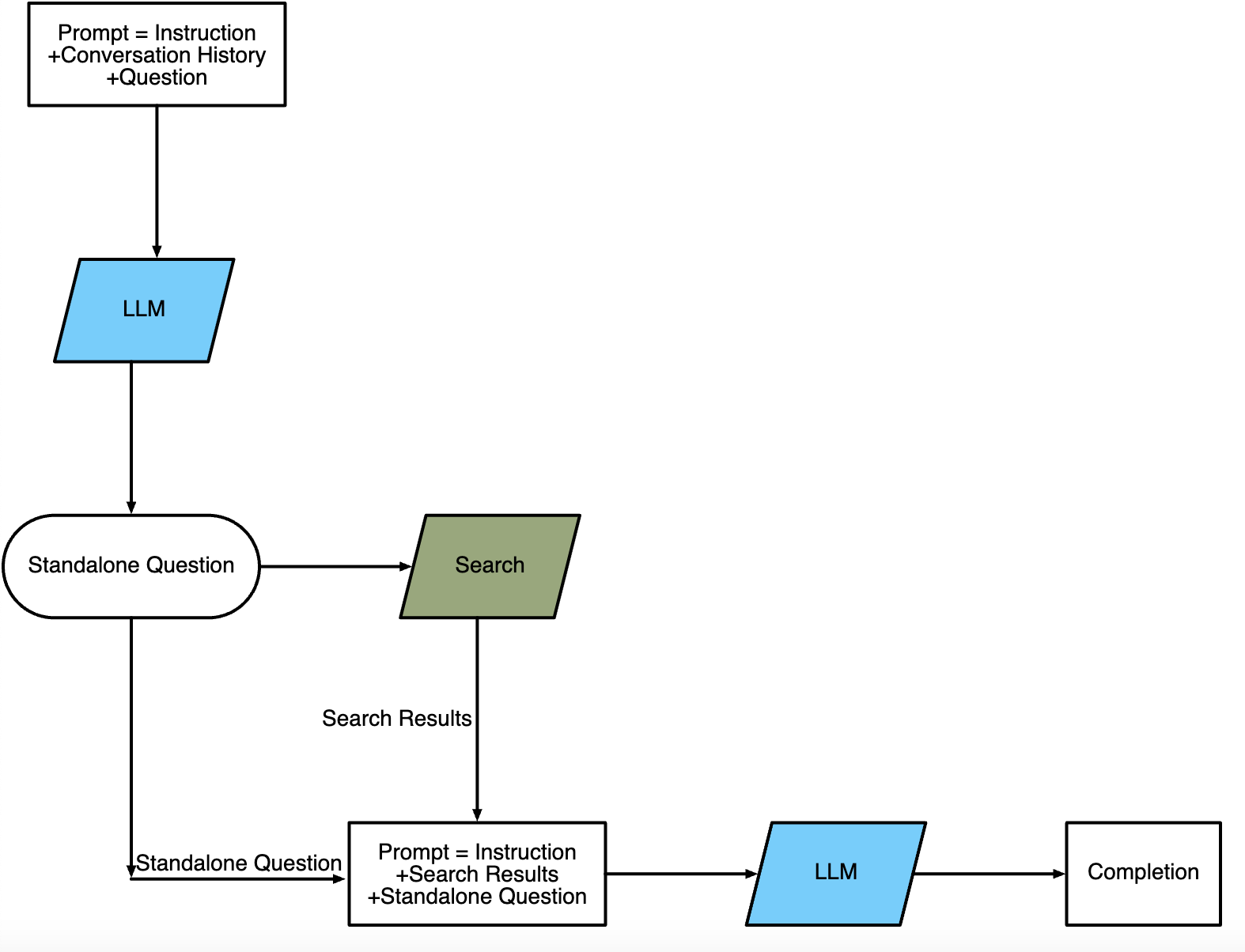
App: WebChatGPT
WebChatGPT is a technology that uses the power of large language models (LLMs) to provide conversational responses to users. It works by taking a user’s question and searching the internet for relevant search results, which are then used to generate a prompt for an LLM to generate an answer. However, WebChatGPT goes one step further than WebGPT by incorporating the conversation history into the process. WebChatGPT uses the current question and the conversation history to create a standalone question that is sent to the internet to search for more relevant information. This standalone question is then used to generate a new prompt for the LLM to generate an answer. By incorporating the conversation history into the process, WebChatGPT is able to provide more personalized and relevant answers to users’ questions.
history = [{
"human": "Who won fifa 2022?",
"ai": "Argentina won the FIFA World Cup 2022."
}]
instruction="Given the following conversation and a follow up question, rephrase the follow up question to be a standalone question."
current_ask="""Chat History:
{chat_history}
Follow Up Input: {question}
Standalone question:"""
question = "what was the final score of the game?"
chat_history = "\n".join(["human: {human}\nai: {ai}".format(**h) for h in history])
prompt = Prompt(instruction=instruction, current_ask=current_ask)
print(prompt.get(chat_history=chat_history, question=question))
Given the following conversation and a follow up question, rephrase the follow up question to be a standalone question.
Chat History:
human: Who won fifa 2022?
ai: Argentina won the FIFA World Cup 2022.
Follow Up Input: what was the final score of the game?
Standalone question:
standalone_question = llm(prompt.get(chat_history=chat_history, question=question))
standalone_question
'What was the final score of the FIFA World Cup 2022 final?'
instruction="Use the following pieces of context to answer the question at the end. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer."
current_ask = "context:{context}\n\nquestion:{question}\nAnswer:"
prompt = Prompt(instruction=instruction, current_ask=current_ask)
# standalone question as new question
question = standalone_question
context = search_internet(question)
print(prompt.get(context=context, question=question))
Use the following pieces of context to answer the question at the end. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.
context:Title: Who won the 2022 FIFA World Cup? Final score, result and highlights ...
Body: Argentina are the world champions. From the moment Lionel Messi put the Copa America holders ahead in the 23rd minute of the 2022 FIFA World Cup final against France, Lionel Scaloni's side looked ...
Title: Argentina wins World Cup final against France in penalty shootout
Body: Argentina won the 2022 World Cup final against France, beating the defending champion during a penalty kick shootout after the teams reached full time with a 3-3 tie. The game had headed into 30 ...
Title: FIFA World Cup 2022: All results, scores and points table
Body: The FIFA World Cup 2022 in Qatar saw a total of 32 top national teams from five different confederations vie for the title of football world champions from November 20 to December 18.. The 2022 FIFA World Cup followed a familiar format with the 32 teams divided into eight groups - Group A to H - of four teams each. The teams in each group competed in a single-headed round-robin format in the ...
question:What was the final score of the FIFA World Cup 2022 final?
Answer:
llm(prompt.get(context=context, question=question))
'The final score of the FIFA World Cup 2022 final was 3-3, and Argentina won the game against France in a penalty shootout.'
Reference
- Initial 2020 GPT-3, large-scale pretraining
- https://learnprompting.org/docs/intro
- https://humanloop.com/blog/prompt-engineering-101
- https://github.com/dair-ai/Prompt-Engineering-Guide
- https://langchain.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/agents.html
- https://langchain.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/chains/getting_started.html
Cited as
@article{kumar2023llmpromptmastering,
title = "Mastering Language Models: Dive into the World of LLM Prompts",
author = "Kumar, Ankur",
journal = "ankur3107.github.io",
year = "2023",
url = "https://ankur3107.github.io/blogs/mastering-llm-prompts/"
}

Comments