LLM is All You Need
Large Language Model
A Large Language Model (LLM) is a type of machine learning model designed to process and generate natural language text. LLMs are typically based on neural networks, a type of artificial intelligence that is inspired by the structure and function of the human brain.
The primary characteristic of LLMs is their size and complexity. These models are typically trained on vast amounts of text data, such as entire books or web pages, and are capable of generating high-quality text that is indistinguishable from human-written text. LLMs are used in a wide variety of natural language processing (NLP) tasks, such as language translation, text summarization, and chatbots.
They have also been used to generate creative writing, such as poems and stories, and have even been used to generate entirely new text-based games. Some examples of popular LLMs include OpenAI’s ChatGPT, GPT-4, GPT-3.5 i.e. These models have achieved remarkable performance on a wide range of NLP tasks and are considered to be some of the most advanced AI systems in existence today.
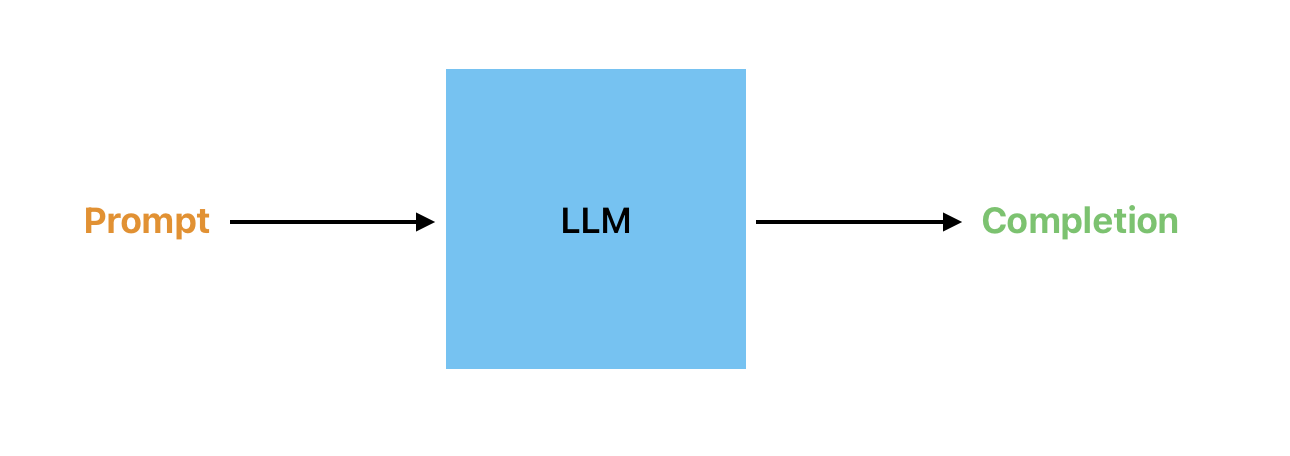
How to generate text
Generating text with an LLM typically involves providing the model with a seed piece of text, known as a prompt, and letting it generate the rest of the text based on the patterns and trends it has learned during training.
How can we use LLM for NLP task
LLMs can be used for a variety of NLP tasks, such as language translation, text summarization, and sentiment analysis. One popular use case is in chatbots, where LLMs can generate responses that are indistinguishable from those of a human operator. LLMs can also be used to analyze large amounts of text data, such as social media feeds or customer reviews, to identify patterns and trends that would be difficult for a human to detect.
To generate text using an LLM, the model must be provided with a seed piece of text known as a prompt. The prompt can be a sentence or a paragraph, and it should be related to the text that the model is expected to generate. The LLM will use the prompt as a starting point and generate new text based on the patterns and trends it has learned during training. The length and complexity of the generated text can be controlled by adjusting the parameters of the model. The generated text can then be evaluated and refined as necessary to ensure that it meets the desired quality and accuracy standards.
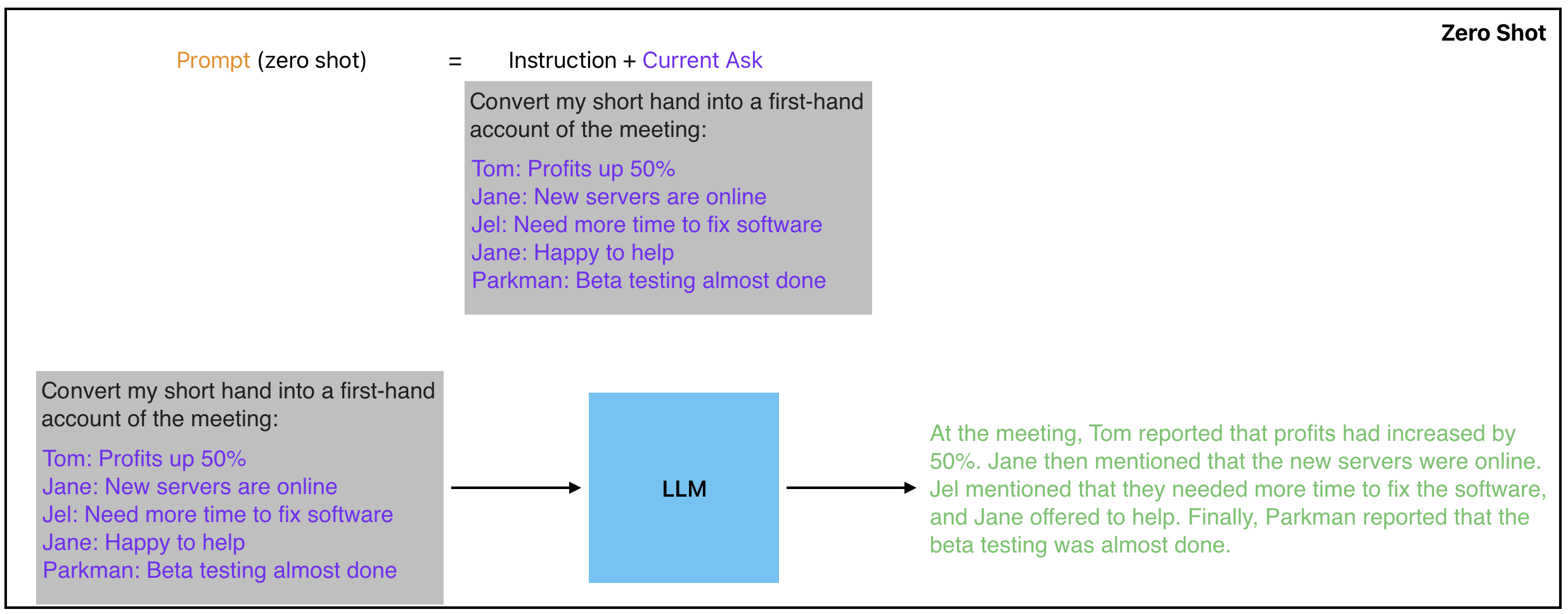
Zero Shot Prompting
Zero-shot prompting is particularly useful when there is no existing training data available for a specific task. By providing the model with a few simple instructions and an example of the desired output, the LLM can generate high-quality text that is tailored to the specific task at hand. This technique has been used in a wide range of applications, from language translation to text summarization, and has been shown to be highly effective in many cases.
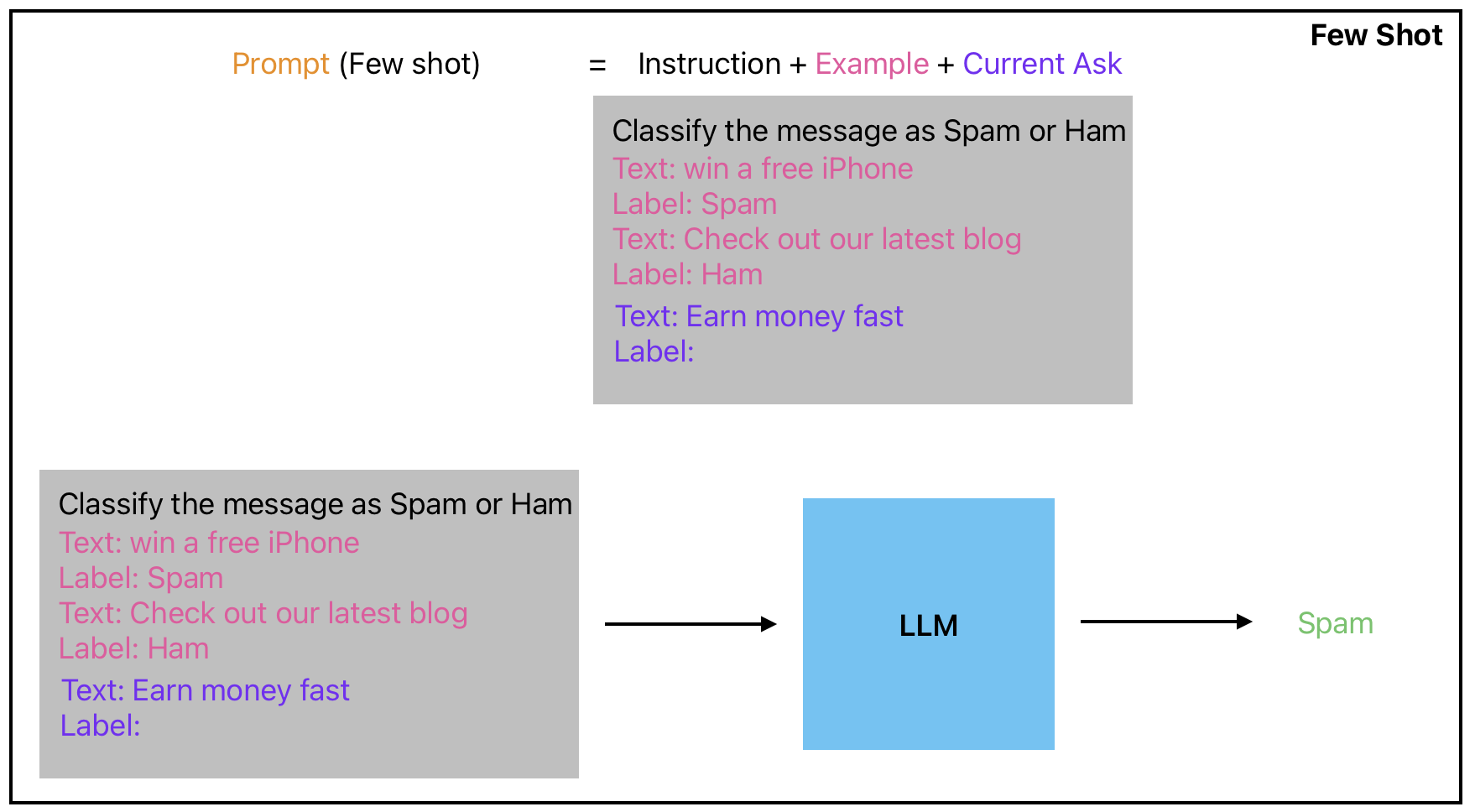
Few Shot Prompting
Few-shot prompting is another technique that can be used to generate text with an LLM. This technique involves providing the model with a few examples of the desired output, along with some instructions and context about the specific task or domain. The LLM can then generate new text that is tailored to the specific task or domain, even if it has not been specifically trained on that task or domain. This technique has been shown to be highly effective in many cases and can be used in a wide range of NLP applications.
Prompt Chaining
Prompt chaining is a technique that involves using the output of one LLM as the input to another LLM. This technique can be used to generate highly complex and nuanced pieces of text, such as long-form articles or stories.
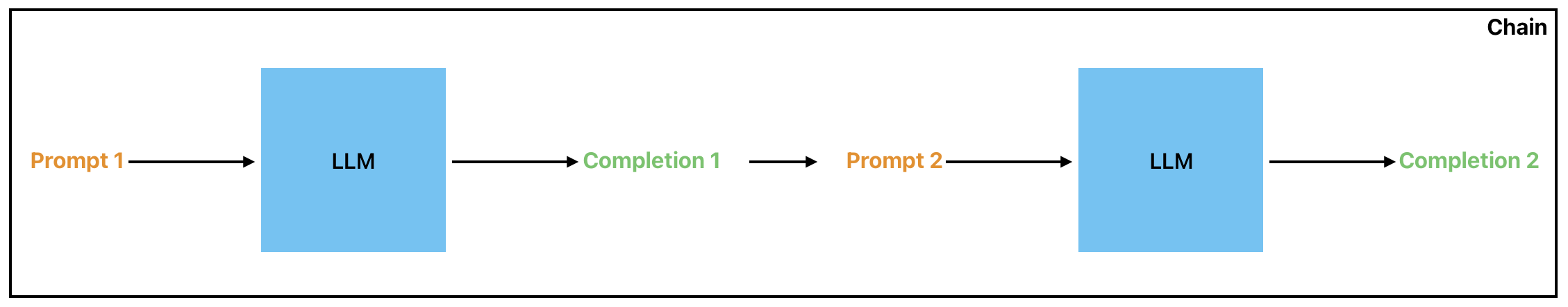
LLM - LLM Chain
To use prompt chaining, the first LLM is provided with an initial prompt and generates some text. This text is then used as the prompt for a second LLM, which generates more text based on the patterns and trends it has learned during training. This process can be repeated multiple times, with each LLM generating increasingly complex and refined pieces of text.
Prompt chaining can be a highly effective technique for generating high-quality text, but it requires careful planning and execution to ensure that the final output meets the desired quality and accuracy standards.
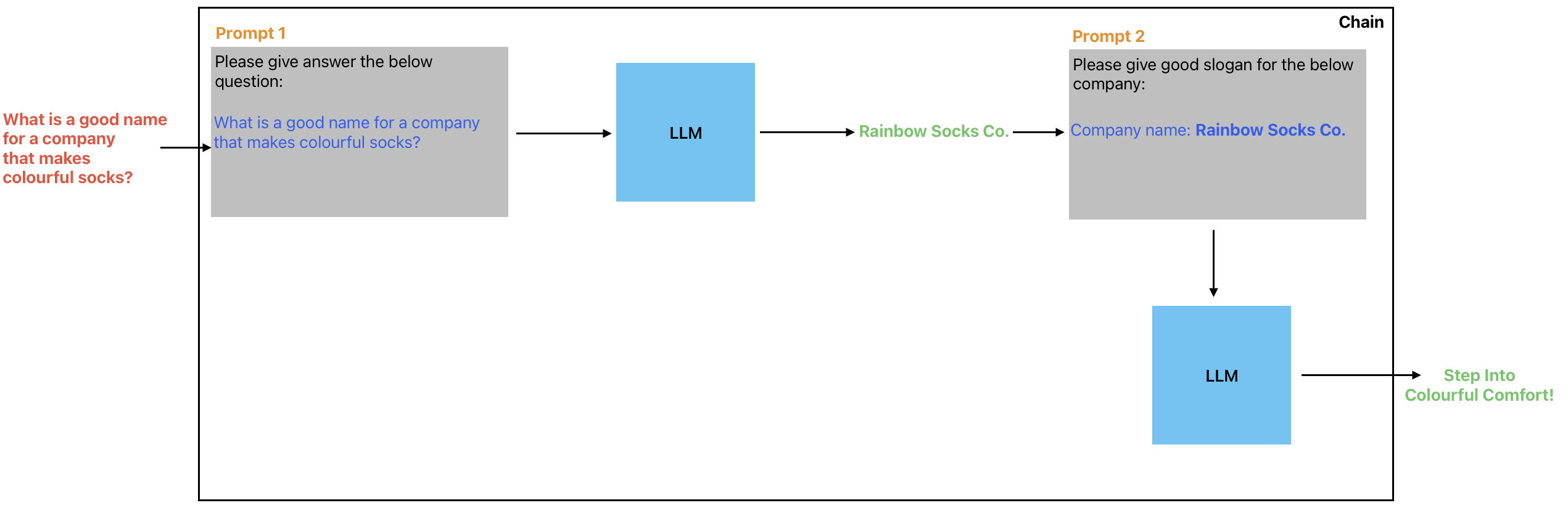
Tool - LLM Chain
Prompt chaining can also be used to retrieve information from a search engine or dataset and then use that information to generate a response or answer to a particular query or prompt. This technique is often used in chatbots and other conversational AI applications, where the model needs to be able to understand and respond to a wide range of user queries and requests. By chaining together multiple LLMs, each specialized for a particular type of information or task, it is possible to create highly sophisticated AI systems that can generate high-quality responses to a wide range of queries and requests.
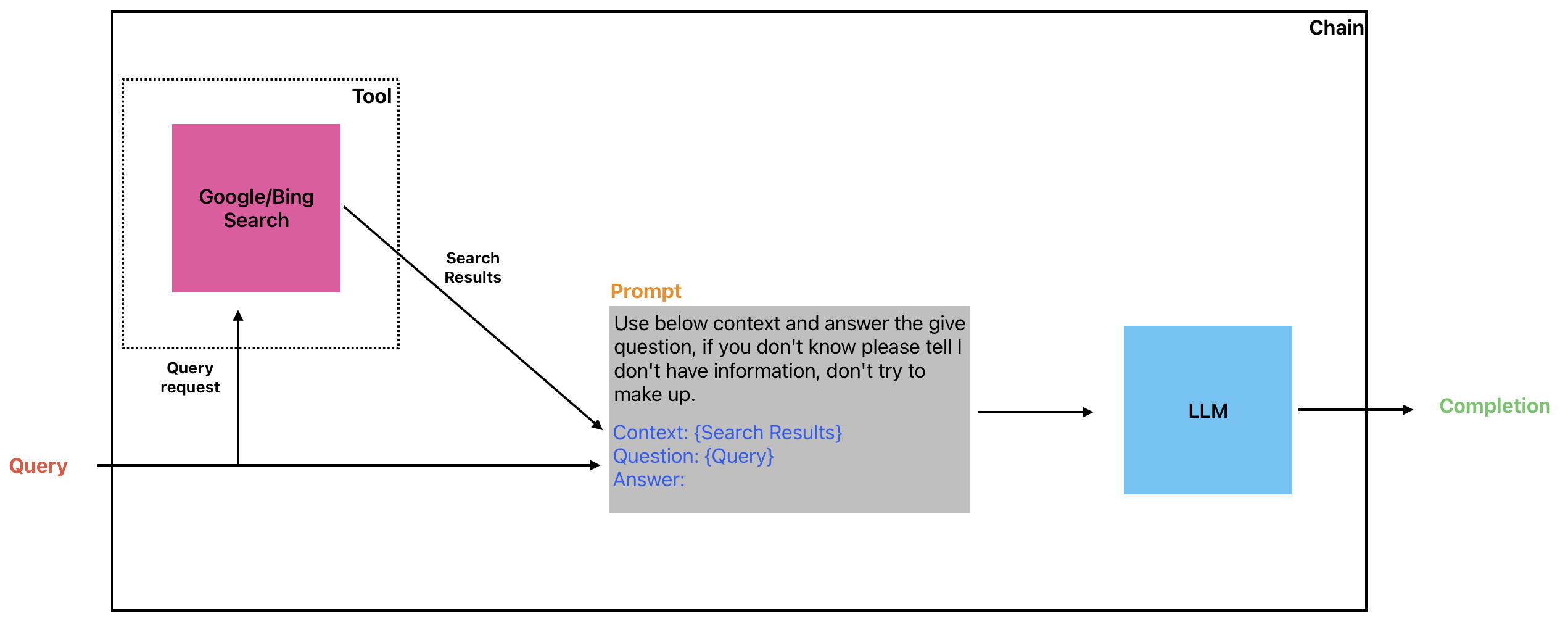
Prompt Agenting
Certain applications may not always follow a pre-determined sequence of calls to language models (LLMs) or other tools. Instead, they may require an adaptive sequence that depends on the user’s input. To achieve this, a “prompt agent” with access to a range of tools can be used. The prompt agent can analyze the user’s input and determine which of the available tools, if any, are best suited for processing the input.
Self-Ask Prompting
Self-ask is a method used to improve the performance of language models in compositional reasoning tasks. It involves having the model explicitly ask and answer follow-up questions before answering the initial question. This method, in combination with elective prompting such as chain of thought, narrows the compositionally gap and improves accuracy.
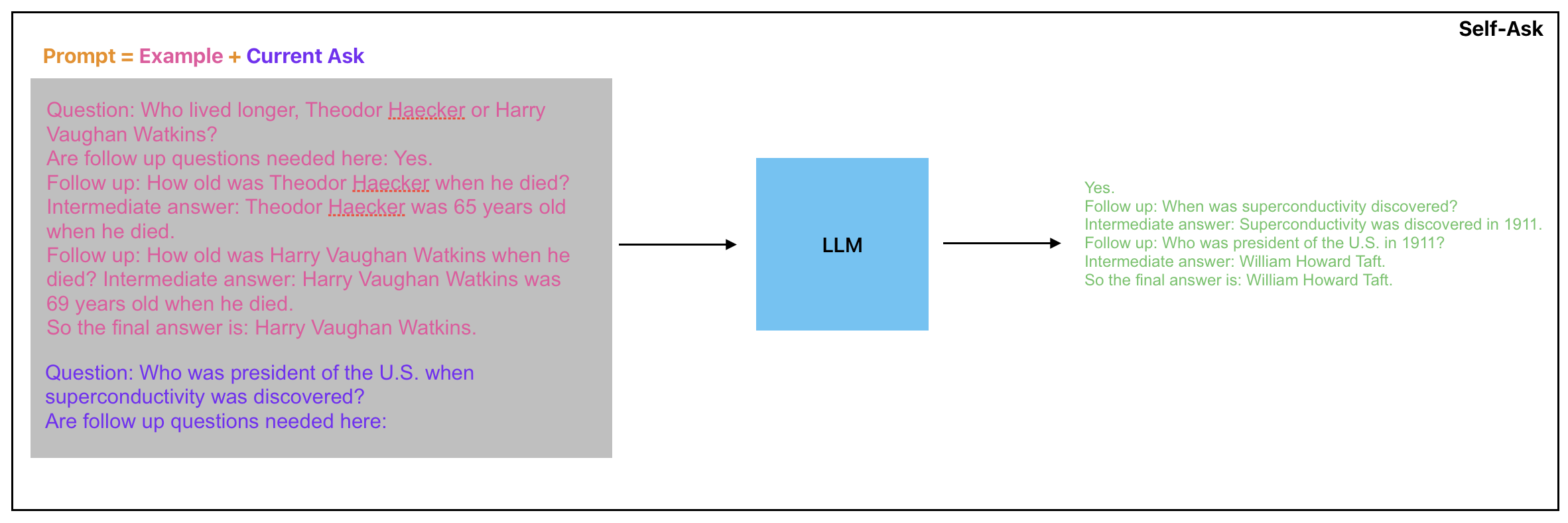
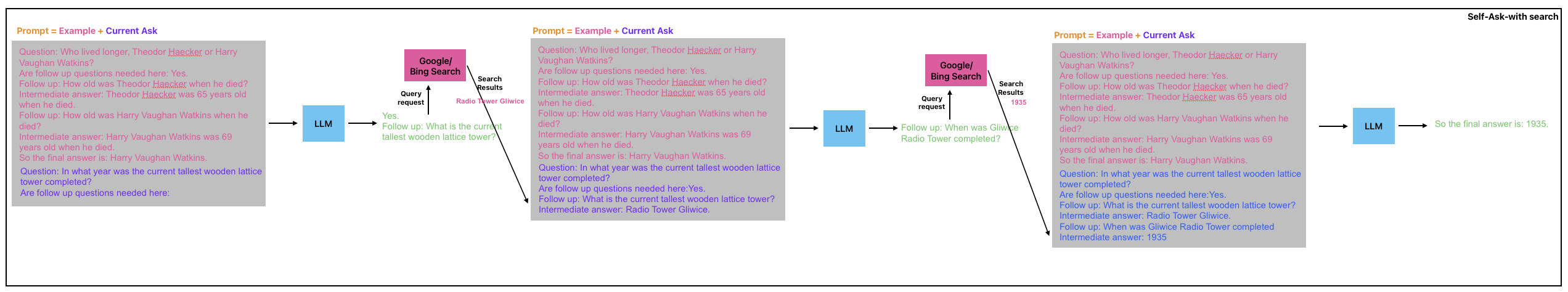
Self-Ask with Search Prompting
The structured prompting of self-ask also allows for the easy integration of a search engine to answer follow-up questions.
TLDR;
The Large Language Model (LLM) is a type of machine learning model that processes and generates natural language text based on neural networks, using a seed piece of text called a prompt. LLMs can be used in various natural language processing tasks, such as language translation, text summarization, and sentiment analysis, and can even generate creative writing. Techniques like zero-shot prompting, few-shot prompting, and prompt chaining can be used to improve the performance of LLMs. Additionally, prompt agenting, self-ask prompting, and self-ask with search prompting can be used to enhance the accuracy of LLMs in compositional reasoning tasks.
Reference
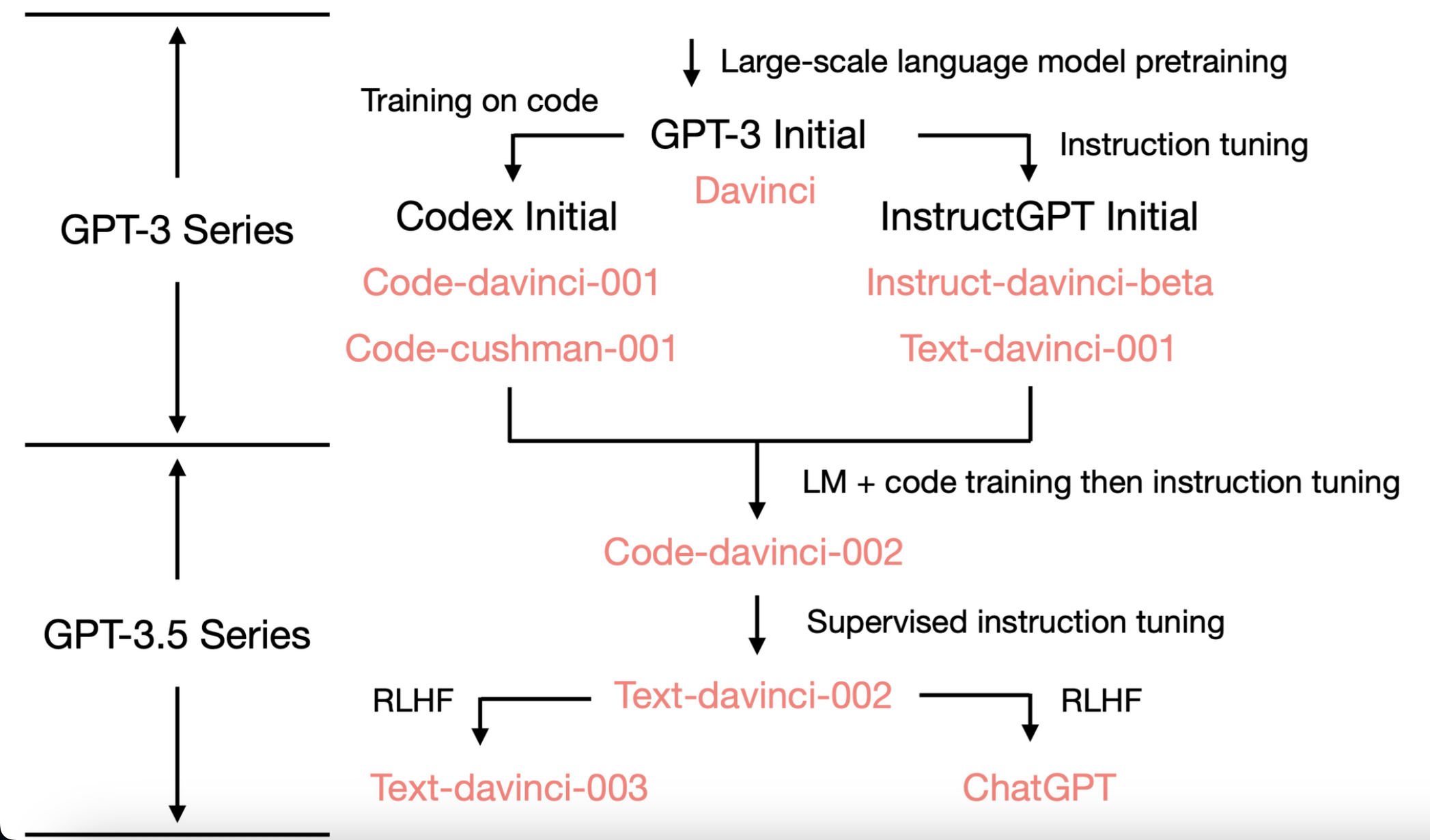
- Initial 2020 GPT-3, large-scale pretraining
- https://learnprompting.org/docs/intro
- https://humanloop.com/blog/prompt-engineering-101
- https://github.com/dair-ai/Prompt-Engineering-Guide
- https://langchain.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/agents.html
- https://langchain.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/chains/getting_started.html
Cited as
@article{kumar2023llmisallyouneed,
title = "LLM is All You Need",
author = "Kumar, Ankur",
journal = "ankur3107.github.io",
year = "2023",
url = "https://ankur3107.github.io/blogs/llm-is-all-you-need/"
}